


| The World Factbook | ||


|
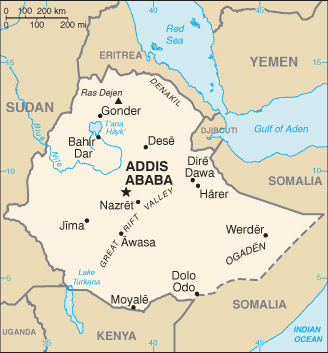
Ethiopia |

|
|
| Introduction | Ethiopia |
|
Background:
|
Unique among African countries, the ancient Ethiopian monarchy maintained its freedom from colonial rule with the exception of the 1936-41 Italian occupation during World War II. In 1974, a military junta, the Derg, deposed Emperor Haile SELASSIE (who had ruled since 1930) and established a socialist state. Torn by bloody coups, uprisings, wide-scale drought, and massive refugee problems, the regime was finally toppled in 1991 by a coalition of rebel forces, the Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front (EPRDF). A constitution was adopted in 1994, and Ethiopia's first multiparty elections were held in 1995. A border war with Eritrea late in the 1990s ended with a peace treaty in December 2000. The Eritrea-Ethiopia Border Commission in November 2007 remotely demarcated the border by geographical coordinates, but final demarcation of the boundary on the ground is currently on hold because of Ethiopian objections to an international commission's finding requiring it to surrender territory considered sensitive to Ethiopia. |
| Geography | Ethiopia |
|
Location:
|
Eastern Africa, west of Somalia |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
8 00 N, 38 00 E |
|
Map references:
|
Africa |
|
Area:
|
total: 1,127,127 sq km
land: 1,119,683 sq km water: 7,444 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
slightly less than twice the size of Texas |
|
Land boundaries:
|
total: 5,328 km
border countries: Djibouti 349 km, Eritrea 912 km, Kenya 861 km, Somalia 1,600 km, Sudan 1,606 km |
|
Coastline:
|
0 km (landlocked) |
|
Maritime claims:
|
none (landlocked) |
|
Climate:
|
tropical monsoon with wide topographic-induced variation |
|
Terrain:
|
high plateau with central mountain range divided by Great Rift Valley |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: Denakil Depression -125 m
highest point: Ras Dejen 4,533 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
small reserves of gold, platinum, copper, potash, natural gas, hydropower |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 10.01%
permanent crops: 0.65% other: 89.34% (2005) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
2,900 sq km (2003) |
|
Total renewable water resources:
|
110 cu km (1987) |
|
Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):
|
total: 5.56 cu km/yr (6%/0%/94%)
per capita: 72 cu m/yr (2002) |
|
Natural hazards:
|
geologically active Great Rift Valley susceptible to earthquakes, volcanic eruptions; frequent droughts |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
deforestation; overgrazing; soil erosion; desertification; water shortages in some areas from water-intensive farming and poor management |
|
Environment - international agreements:
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Ozone Layer Protection
signed, but not ratified: Environmental Modification, Law of the Sea |
|
Geography - note:
|
landlocked - entire coastline along the Red Sea was lost with the de jure independence of Eritrea on 24 May 1993; the Blue Nile, the chief headstream of the Nile by water volume, rises in T'ana Hayk (Lake Tana) in northwest Ethiopia; three major crops are believed to have originated in Ethiopia: coffee, grain sorghum, and castor bean |
| People | Ethiopia |
|
Population:
|
82,544,840
note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2008 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 46% (male 18,922,334/female 19,017,593)
15-64 years: 51.4% (male 20,749,002/female 21,656,509) 65 years and over: 2.7% (male 947,323/female 1,252,077) (2008 est.) |
|
Median age:
|
total: 16.9 years
male: 16.6 years female: 17.2 years (2008 est.) |
|
Population growth rate:
|
3.212% (2008 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|
43.97 births/1,000 population (2008 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|
11.83 deaths/1,000 population (2008 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|
NA
note: repatriation of Ethiopian refugees residing in Sudan is expected to continue for several years; some Sudanese, Somali, and Eritrean refugees, who fled to Ethiopia from the fighting or famine in their own countries, continue to return to their homes (2008 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 0.96 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.76 male(s)/female total population: 0.97 male(s)/female (2008 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
total: 82.64 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 94.08 deaths/1,000 live births female: 70.87 deaths/1,000 live births (2008 est.) |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 54.99 years
male: 52.54 years female: 57.51 years (2008 est.) |
|
Total fertility rate:
|
6.17 children born/woman (2008 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|
4.4% (2003 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
1.5 million (2003 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
120,000 (2003 est.) |
|
Major infectious diseases:
|
degree of risk: high
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A and E, and typhoid fever vectorborne diseases: malaria respiratory disease: meningococcal meningitis animal contact disease: rabies water contact disease: schistosomiasis (2008) |
|
Nationality:
|
noun: Ethiopian(s)
adjective: Ethiopian |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
Oromo 32.1%, Amara 30.1%, Tigraway 6.2%, Somalie 5.9%, Guragie 4.3%, Sidama 3.5%, Welaita 2.4%, other 15.4% (1994 census) |
|
Religions:
|
Christian 60.8% (Orthodox 50.6%, Protestant 10.2%), Muslim 32.8%, traditional 4.6%, other 1.8% (1994 census) |
|
Languages:
|
Amarigna 32.7%, Oromigna 31.6%, Tigrigna 6.1%, Somaligna 6%, Guaragigna 3.5%, Sidamigna 3.5%, Hadiyigna 1.7%, other 14.8%, English (major foreign language taught in schools) (1994 census) |
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 42.7% male: 50.3% female: 35.1% (2003 est.) |
|
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):
|
total: 8 years
male: 8 years female: 7 years (2007) |
|
Education expenditures:
|
6% of GDP (2006) |
| Government | Ethiopia |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia
conventional short form: Ethiopia local long form: Ityop'iya Federalawi Demokrasiyawi Ripeblik local short form: Ityop'iya former: Abyssinia, Italian East Africa abbreviation: FDRE |
|
Government type:
|
federal republic |
|
Capital:
|
name: Addis Ababa
geographic coordinates: 9 02 N, 38 42 E time difference: UTC+3 (8 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time) |
|
Administrative divisions:
|
9 ethnically based states (kililoch, singular - kilil) and 2 self-governing administrations* (astedaderoch, singular - astedader); Adis Abeba* (Addis Ababa), Afar, Amara (Amhara), Binshangul Gumuz, Dire Dawa*, Gambela Hizboch (Gambela Peoples), Hareri Hizb (Harari People), Oromiya (Oromia), Sumale (Somali), Tigray, Ye Debub Biheroch Bihereseboch na Hizboch (Southern Nations, Nationalities and Peoples) |
|
Independence:
|
oldest independent country in Africa and one of the oldest in the world - at least 2,000 years |
|
National holiday:
|
National Day (defeat of MENGISTU regime), 28 May (1991) |
|
Constitution:
|
ratified 8 December 1994, effective 22 August 1995 |
|
Legal system:
|
based on civil law; currently transitional mix of national and regional courts; has not accepted compulsory ICJ jurisdiction |
|
Suffrage:
|
18 years of age; universal |
|
Executive branch:
|
chief of state: President GIRMA Woldegiorgis (since 8 October 2001)
head of government: Prime Minister MELES Zenawi (since August 1995) cabinet: Council of Ministers as provided for in the December 1994 constitution; ministers are selected by the prime minister and approved by the House of People's Representatives elections: president elected by the House of People's Representatives for a six-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held 9 October 2007 (next to be held in October 2013); prime minister designated by the party in power following legislative elections election results: GIRMA Woldegiorgis elected president; percent of vote by the House of People's Representatives - 79% |
|
Legislative branch:
|
bicameral Parliament consists of the House of Federation (or upper chamber responsible for interpreting the constitution and federal-regional issues) (108 seats; members are chosen by state assemblies to serve five-year terms) and the House of People's Representatives (or lower chamber responsible for passing legislation) (547 seats; members are directly elected by popular vote from single-member districts to serve five-year terms)
elections: last held 15 May 2005 (next to be held in 2010) election results: percent of vote - NA; seats by party - EPRDF 327, CUD 109, UEDF 52, SPDP 23, OFDM 11, BGPDUF 8, ANDP 8, independent 1, others 6, undeclared 2 note: some seats still remain vacant as detained opposition MPs did not take their seats |
|
Judicial branch:
|
Federal Supreme Court (the president and vice president of the Federal Supreme Court are recommended by the prime minister and appointed by the House of People's Representatives; for other federal judges, the prime minister submits to the House of People's Representatives for appointment candidates selected by the Federal Judicial Administrative Council) |
|
Political parties and leaders:
|
Afar National Democratic Party or ANDP; Benishangul Gumuz People's Democratic Unity Front or BGPDUF [Mulualem BESSE]; Coalition for Unity and Democratic Party or CUDP [AYELE Chamisso] (awarded to AYELE by the National Electoral Board on 11 January 2008, but AYELE has virtually no support among former CUD MPs, other CUD MPs must now be affiliated with their original CUD-precursor parties); Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front or EPRDF [MELES Zenawi] (an alliance of Amhara National Democratic Movement or ANDM, Oromo People's Democratic Organization or OPDO, the South Ethiopian People's Democratic Front or SEPDF, and Tigrayan Peoples' Liberation Front or TPLF); Gurage Nationalities' Democratic Movement or GNDM; Oromo Federalist Democratic Movement or OFDM [BULCHA Demeksa]; Omoro People's Congress or OPC [IMERERA Gudina]; Somali People's Democratic Party or SPDP; United Ethiopian Democratic Forces or UEDF [BEYENE Petros] |
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|
Ethiopian People's Patriotic Front or EPPF; Ogaden National Liberation Front or ONLF; Oromo Liberation Front or OLF [DAOUD Ibsa] |
|
International organization participation:
|
ACP, AfDB, AU, COMESA, FAO, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IGAD, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM (observer), IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, NAM, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMIL, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO (observer) |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Samuel ASSEFA
chancery: 3506 International Drive NW, Washington, DC 20008 telephone: [1] (202) 364-1200 FAX: [1] (202) 587-0195 consulate(s) general: Los Angeles consulate(s): New York |
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Donald Y. YAMAMOTO
embassy: Entoto Street, Addis Ababa mailing address: P. O. Box 1014, Addis Ababa telephone: [251] 11-517-40-00 FAX: [251] 11-517-40-01 |
|
Flag description:
|
three equal horizontal bands of green (top), yellow, and red with a yellow pentagram and single yellow rays emanating from the angles between the points on a light blue disk centered on the three bands; Ethiopia is the oldest independent country in Africa, and the three main colors of her flag were so often adopted by other African countries upon independence that they became known as the pan-African colors |
| Economy | Ethiopia |
|
Economy - overview:
|
Ethiopia's poverty-stricken economy is based on agriculture, accounting for almost half of GDP, 60% of exports, and 80% of total employment. The agricultural sector suffers from frequent drought and poor cultivation practices. Coffee is critical to the Ethiopian economy with exports of some $350 million in 2006, but historically low prices have seen many farmers switching to qat to supplement income. The war with Eritrea in 1998-2000 and recurrent drought have buffeted the economy, in particular coffee production. In November 2001, Ethiopia qualified for debt relief from the Highly Indebted Poor Countries (HIPC) initiative, and in December 2005 the IMF voted to forgive Ethiopia's debt to the body. Under Ethiopia's constitution, the state owns all land and provides long-term leases to the tenants; the system continues to hamper growth in the industrial sector as entrepreneurs are unable to use land as collateral for loans. Drought struck again late in 2002, leading to a 3.3% decline in GDP in 2003. Normal weather patterns helped agricultural and GDP growth recover during 2004-07. |
|
GDP (purchasing power parity):
|
$56.05 billion (2007 est.) |
|
GDP (official exchange rate):
|
$19.43 billion (2007 est.) |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
11.1% (2007 est.) |
|
GDP - per capita (PPP):
|
$700 (2007 est.) |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
agriculture: 47%
industry: 13.2% services: 39.8% (2007 est.) |
|
Labor force:
|
27.27 million (1999) |
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|
agriculture: 80%
industry: 8% services: 12% (1985) |
|
Unemployment rate:
|
NA% |
|
Population below poverty line:
|
38.7% (FY05/06 est.) |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: 3.9%
highest 10%: 25.5% (2000) |
|
Distribution of family income - Gini index:
|
30 (2000) |
|
Investment (gross fixed):
|
25.9% of GDP (2007 est.) |
|
Budget:
|
revenues: $3.231 billion
expenditures: $3.785 billion (2007 est.) |
|
Fiscal year:
|
8 July - 7 July |
|
Public debt:
|
44.5% of GDP (2007 est.) |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
17.2% (2007 est.) |
|
Commercial bank prime lending rate:
|
7% (31 December 2006) |
|
Stock of money:
|
$3.651 billion (31 December 2006) |
|
Stock of quasi money:
|
$3.258 billion (31 December 2007) |
|
Stock of domestic credit:
|
$6.694 billion (31 December 2006) |
|
Agriculture - products:
|
cereals, pulses, coffee, oilseed, cotton, sugarcane, potatoes, qat, cut flowers; hides, cattle, sheep, goats; fish |
|
Industries:
|
food processing, beverages, textiles, leather, chemicals, metals processing, cement |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
11% (2007 est.) |
|
Electricity - production:
|
3.268 billion kWh (2006 est.) |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
2.941 billion kWh (2006 est.) |
|
Electricity - exports:
|
0 kWh (2007 est.) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|
0 kWh (2007 est.) |
|
Electricity - production by source:
|
fossil fuel: 1.3%
hydro: 97.6% nuclear: 0% other: 1.2% (2001) |
|
Oil - production:
|
7.334 bbl/day (2007 est.) |
|
Oil - consumption:
|
30,450 bbl/day (2006 est.) |
|
Oil - exports:
|
0 bbl/day (2005) |
|
Oil - imports:
|
29,820 bbl/day (2005) |
|
Oil - proved reserves:
|
428,000 bbl (1 January 2008 est.) |
|
Natural gas - production:
|
0 cu m (2007 est.) |
|
Natural gas - consumption:
|
0 cu m (2007 est.) |
|
Natural gas - exports:
|
0 cu m (2007 est.) |
|
Natural gas - imports:
|
0 cu m (2007 est.) |
|
Natural gas - proved reserves:
|
24.92 billion cu m (1 January 2008 est.) |
|
Current account balance:
|
-$826.8 million (2007 est.) |
|
Exports:
|
$1.288 billion f.o.b. (2007 est.) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|
coffee, qat, gold, leather products, live animals, oilseeds |
|
Exports - partners:
|
Germany 8.2%, Saudi Arabia 7%, US 6.9%, Djibouti 6.6%, China 6.5%, Italy 6.5%, Japan 5.9%, Netherlands 4.8% (2007) |
|
Imports:
|
$5.165 billion f.o.b. (2007 est.) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|
food and live animals, petroleum and petroleum products, chemicals, machinery, motor vehicles, cereals, textiles |
|
Imports - partners:
|
Saudi Arabia 17%, China 15.9%, India 7.8%, Italy 5.1% (2007) |
|
Economic aid - recipient:
|
$1.6 billion (FY05/06) |
|
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
|
$1.294 billion (31 December 2007 est.) |
|
Debt - external:
|
$2.621 billion (31 December 2007 est.) |
|
Market value of publicly traded shares:
|
$NA |
|
Currency (code):
|
birr (ETB) |
|
Currency code:
|
ETB |
|
Exchange rates:
|
birr (ETB) per US dollar - 8.96 (2007), 8.69 (2006), 8.68 (2005), 8.6356 (2004), 8.5997 (2003)
note: since 24 October 2001, exchange rates are determined on a daily basis via interbank transactions regulated by the Central Bank |
| Communications | Ethiopia |
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
880,100 (2007) |
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
1.208 million (2007) |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: inadequate telephone system; the number of fixed lines and mobile telephones is increasing from a very small base; combined fixed and mobile-cellular teledensity is only about 2 per 100 persons
domestic: open-wire; microwave radio relay; radio communication in the HF, VHF, and UHF frequencies; 2 domestic satellites provide the national trunk service international: country code - 251; open-wire to Sudan and Djibouti; microwave radio relay to Kenya and Djibouti; satellite earth stations - 3 Intelsat (1 Atlantic Ocean and 2 Pacific Ocean) |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
AM 8, FM 0, shortwave 1 (2001) |
|
Radios:
|
15.2 million (2002) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
1 (plus 24 repeaters) (2001) |
|
Televisions:
|
682,000 (2002) |
|
Internet country code:
|
.et |
|
Internet hosts:
|
128 (2008) |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
1 (2002) |
|
Internet users:
|
291,000 (2007) |
| Transportation | Ethiopia |
|
Airports:
|
84 (2007) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 15
over 3,047 m: 3 2,438 to 3,047 m: 5 1,524 to 2,437 m: 5 914 to 1,523 m: 1 under 914 m: 1 (2007) |
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|
total: 69
over 3,047 m: 3 2,438 to 3,047 m: 5 1,524 to 2,437 m: 11 914 to 1,523 m: 29 under 914 m: 21 (2007) |
|
Railways:
|
total: 699 km (Ethiopian segment of the Addis Ababa-Djibouti railroad)
narrow gauge: 699 km 1.000-m gauge note: railway under joint control of Djibouti and Ethiopia but remains largely inoperable (2006) |
|
Roadways:
|
total: 36,469 km
paved: 6,980 km unpaved: 29,489 km (2004) |
|
Merchant marine:
|
total: 9
by type: cargo 8, roll on/roll off 1 (2008) |
|
Ports and terminals:
|
Ethiopia is landlocked and uses ports of Djibouti in Djibouti and Berbera in Somalia |
| Military | Ethiopia |
|
Military branches:
|
Ethiopian National Defense Force (ENDF): Ground Forces, Ethiopian Air Force (ETAF) (2008)
note: Ethiopia is landlocked and has no navy; following the secession of Eritrea, Ethiopian naval facilities remained in Eritrean possession |
|
Military service age and obligation:
|
18 years of age for compulsory and voluntary military service; theoretically, no compulsory military service, but the military can conduct call-ups when necessary and compliance is compulsory (2008) |
|
Manpower available for military service:
|
males age 16-49: 17,666,967
females age 16-49: 17,530,211 (2008 est.) |
|
Manpower fit for military service:
|
males age 16-49: 10,060,775
females age 16-49: 9,854,710 (2008 est.) |
|
Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:
|
male: 887,061
female: 896,048 (2008 est.) |
|
Military expenditures:
|
3% of GDP (2006) |
| Transnational Issues | Ethiopia |
|
Disputes - international:
|
Eritrea and Ethiopia agreed to abide by the 2002 Eritrea-Ethiopia Boundary Commission's (EEBC) delimitation decision, but neither party responded to the revised line detailed in the November 2006 EEBC Demarcation Statement; UN Peacekeeping Mission to Ethiopia and Eritrea (UNMEE), which has monitored the 25-km-wide Temporary Security Zone in Eritrea since 2000, is extended for six months in 2007 despite Eritrean restrictions on its operations and reduced force of 17,000; the undemarcated former British administrative line has little meaning as a political separation to rival clans within Ethiopia's Ogaden and southern Somalia's Oromo region; Ethiopian forces invaded southern Somalia and routed Islamist Courts from Mogadishu in January 2007; "Somaliland" secessionists provide port facilities in Berbera and trade ties to landlocked Ethiopia; civil unrest in eastern Sudan has hampered efforts to demarcate the porous boundary with Ethiopia |
|
Refugees and internally displaced persons:
|
refugees (country of origin): 66,980 (Sudan); 16,576 (Somalia); 13,078 (Eritrea)
IDPs: 200,000 (border war with Eritrea from 1998-2000, ethnic clashes in Gambela, and ongoing Ethiopian military counterinsurgency in Somali region; most IDPs are in Tigray and Gambela Provinces) (2007) |
|
Illicit drugs:
|
transit hub for heroin originating in Southwest and Southeast Asia and destined for Europe, as well as cocaine destined for markets in southern Africa; cultivates qat (khat) for local use and regional export, principally to Djibouti and Somalia (legal in all three countries); the lack of a well-developed financial system limits the country's utility as a money laundering center |
|
This page was last updated on 18 December, 2008 |