


| The World Factbook | ||


|
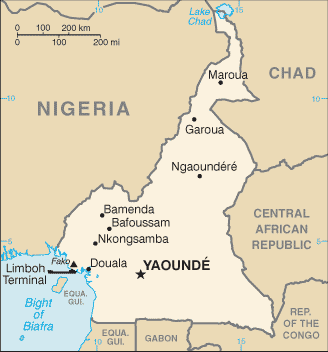
Cameroon |

|
|
| Introduction | Cameroon |
|
Background:
|
The former French Cameroon and part of British Cameroon merged in 1961 to form the present country. Cameroon has generally enjoyed stability, which has permitted the development of agriculture, roads, and railways, as well as a petroleum industry. Despite a slow movement toward democratic reform, political power remains firmly in the hands of President Paul BIYA. |
| Geography | Cameroon |
|
Location:
|
Western Africa, bordering the Bight of Biafra, between Equatorial Guinea and Nigeria |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
6 00 N, 12 00 E |
|
Map references:
|
Africa |
|
Area:
|
total: 475,440 sq km
land: 469,440 sq km water: 6,000 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
slightly larger than California |
|
Land boundaries:
|
total: 4,591 km
border countries: Central African Republic 797 km, Chad 1,094 km, Republic of the Congo 523 km, Equatorial Guinea 189 km, Gabon 298 km, Nigeria 1,690 km |
|
Coastline:
|
402 km |
|
Maritime claims:
|
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm |
|
Climate:
|
varies with terrain, from tropical along coast to semiarid and hot in north |
|
Terrain:
|
diverse, with coastal plain in southwest, dissected plateau in center, mountains in west, plains in north |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
highest point: Fako 4,095 m (on Mt. Cameroon) |
|
Natural resources:
|
petroleum, bauxite, iron ore, timber, hydropower |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 12.54%
permanent crops: 2.52% other: 84.94% (2005) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
260 sq km (2003) |
|
Total renewable water resources:
|
285.5 cu km (2003) |
|
Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):
|
total: 0.99 cu km/yr (18%/8%/74%)
per capita: 61 cu m/yr (2000) |
|
Natural hazards:
|
volcanic activity with periodic releases of poisonous gases from Lake Nyos and Lake Monoun volcanoes |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
waterborne diseases are prevalent; deforestation; overgrazing; desertification; poaching; overfishing |
|
Environment - international agreements:
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
|
Geography - note:
|
sometimes referred to as the hinge of Africa; throughout the country there are areas of thermal springs and indications of current or prior volcanic activity; Mount Cameroon, the highest mountain in Sub-Saharan west Africa, is an active volcano |
| People | Cameroon |
|
Population:
|
18,467,692
note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2008 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 41.1% (male 3,826,232/female 3,757,859)
15-64 years: 55.7% (male 5,164,338/female 5,122,817) 65 years and over: 3.2% (male 274,821/female 321,625) (2008 est.) |
|
Median age:
|
total: 19 years
male: 18.9 years female: 19.2 years (2008 est.) |
|
Population growth rate:
|
2.218% (2008 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|
34.59 births/1,000 population (2008 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|
12.41 deaths/1,000 population (2008 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|
NA (2008 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.02 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 1.01 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.85 male(s)/female total population: 1.01 male(s)/female (2008 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
total: 64.57 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 69.39 deaths/1,000 live births female: 59.62 deaths/1,000 live births (2008 est.) |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 53.3 years
male: 52.54 years female: 54.08 years (2008 est.) |
|
Total fertility rate:
|
4.41 children born/woman (2008 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|
6.9% (2003 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
560,000 (2003 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
49,000 (2003 est.) |
|
Major infectious diseases:
|
degree of risk: very high
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A and E, and typhoid fever vectorborne diseases: malaria and yellow fever water contact disease: schistosomiasis respiratory disease: meningococcal meningitis animal contact disease: rabies (2008) |
|
Nationality:
|
noun: Cameroonian(s)
adjective: Cameroonian |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
Cameroon Highlanders 31%, Equatorial Bantu 19%, Kirdi 11%, Fulani 10%, Northwestern Bantu 8%, Eastern Nigritic 7%, other African 13%, non-African less than 1% |
|
Religions:
|
indigenous beliefs 40%, Christian 40%, Muslim 20% |
|
Languages:
|
24 major African language groups, English (official), French (official) |
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 67.9% male: 77% female: 59.8% (2001 est.) |
|
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):
|
total: 9 years
male: 10 years female: 8 years (2006) |
|
Education expenditures:
|
3.3% of GDP (2006) |
| Government | Cameroon |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: Republic of Cameroon
conventional short form: Cameroon local long form: Republique du Cameroun/Republic of Cameroon local short form: Cameroun/Cameroon former: French Cameroon, British Cameroon, Federal Republic of Cameroon, United Republic of Cameroon |
|
Government type:
|
republic; multiparty presidential regime |
|
Capital:
|
name: Yaounde
geographic coordinates: 3 52 N, 11 31 E time difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time) |
|
Administrative divisions:
|
10 provinces; Adamaoua, Centre, Est, Extreme-Nord, Littoral, Nord, Nord-Ouest, Ouest, Sud, Sud-Ouest |
|
Independence:
|
1 January 1960 (from French-administered UN trusteeship) |
|
National holiday:
|
Republic Day (National Day), 20 May (1972) |
|
Constitution:
|
20 May 1972 approved by referendum, adopted 2 June 1972; revised January 1996 |
|
Legal system:
|
based on French civil law system, with common law influence; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction |
|
Suffrage:
|
20 years of age; universal |
|
Executive branch:
|
chief of state: President Paul BIYA (since 6 November 1982)
head of government: Prime Minister Ephraim INONI (since 8 December 2004) cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president from proposals submitted by the prime minister elections: president elected by popular vote for a seven-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held 11 October 2004 (next to be held by October 2011); prime minister appointed by the president election results: President Paul BIYA reelected; percent of vote - Paul BIYA 70.9%, John FRU NDI 17.4%, Adamou Ndam NJOYA 4.5%, Garga Haman ADJI 3.7% |
|
Legislative branch:
|
unicameral National Assembly or Assemblee Nationale (180 seats; members are elected by direct popular vote to serve five-year terms); note - the president can either lengthen or shorten the term of the legislature
elections: last held 22 July 2007 (next to be held in 2012) election results: percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - RDCP 140, SDF 14, UDC 4, UNDP 4, MP 1, vacant 17; note - vacant seats will be determined in a yet to be scheduled by-election after the Supreme Court nullified results in five districts note: the constitution calls for an upper chamber for the legislature, to be called a Senate, but it has yet to be established |
|
Judicial branch:
|
Supreme Court (judges are appointed by the president); High Court of Justice (consists of nine judges and six substitute judges, elected by the National Assembly) |
|
Political parties and leaders:
|
Cameroonian Democratic Union or UDC [Adamou Ndam NJOYA]; Cameroon People's Democratic Movement or RDPC [Paul BIYA]; Movement for the Defense of the Republic or MDR [Dakole DAISSALA]; Movement for the Liberation and Development of Cameroon or MLDC [Marcel YONDO]; National Union for Democracy and Progress or UNDP [Maigari BELLO BOUBA]; Progressive Movement or MP; Social Democratic Front or SDF [John FRU NDI]; Union of Peoples of Cameroon or UPC [Augustin Frederic KODOCK] |
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|
Human Rights Defense Group [Albert MUKONG, president]; Southern Cameroon National Council [Ayamba Ette OTUN] |
|
International organization participation:
|
ACCT, ACP, AfDB, AU, BDEAC, C, CEMAC, FAO, FZ, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC, ICCt (signatory), ICRM, IDA, IDB, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, NAM, OIC, OIF, OPCW, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNWTO, UPU, WCL, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Joseph FOE-ATANGANA
chancery: 2349 Massachusetts Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008 telephone: [1] (202) 265-8790 FAX: [1] (202) 387-3826 |
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Janet E. GARVEY
embassy: Avenue Rosa Parks, Yaounde mailing address: P. O. Box 817, Yaounde; pouch: American Embassy, US Department of State, Washington, DC 20521-2520 telephone: [237] 2220 15 00; Consular: [237] 2220 16 03 FAX: [237] 2220 16 00 Ext. 4531; Consular FAX: [237] 2220 17 52 branch office(s): Douala |
|
Flag description:
|
three equal vertical bands of green (hoist side), red, and yellow with a yellow five-pointed star centered in the red band
note: uses the popular pan-African colors of Ethiopia |
| Economy | Cameroon |
|
Economy - overview:
|
Because of its modest oil resources and favorable agricultural conditions, Cameroon has one of the best-endowed primary commodity economies in sub-Saharan Africa. Still, it faces many of the serious problems facing other underdeveloped countries, such as a top-heavy civil service and a generally unfavorable climate for business enterprise. Since 1990, the government has embarked on various IMF and World Bank programs designed to spur business investment, increase efficiency in agriculture, improve trade, and recapitalize the nation's banks. In June 2000, the government completed an IMF-sponsored, three-year structural adjustment program; however, the IMF is pressing for more reforms, including increased budget transparency, privatization, and poverty reduction programs. In January 2001, the Paris Club agreed to reduce Cameroon's debt of $1.3 billion by $900 million; debt relief now totals $1.26 billion. International oil and cocoa prices have a significant impact on the economy. |
|
GDP (purchasing power parity):
|
$40.24 billion (2007 est.) |
|
GDP (official exchange rate):
|
$20.65 billion (2007 est.) |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
2.7% (2007 est.) |
|
GDP - per capita (PPP):
|
$2,200 (2007 est.) |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
agriculture: 43.9%
industry: 15.8% services: 40.3% (2007 est.) |
|
Labor force:
|
6.674 million (2007 est.) |
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|
agriculture: 70%
industry: 13% services: 17% (2001 est.) |
|
Unemployment rate:
|
30% (2001 est.) |
|
Population below poverty line:
|
48% (2000 est.) |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: 2.3%
highest 10%: 35.4% (2001) |
|
Distribution of family income - Gini index:
|
44.6 (2001) |
|
Investment (gross fixed):
|
17.3% of GDP (2007 est.) |
|
Budget:
|
revenues: $4.179 billion
expenditures: $3.297 billion (2007 est.) |
|
Fiscal year:
|
1 July - 30 June |
|
Public debt:
|
15.5% of GDP (2007 est.) |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
1.1% (2007 est.) |
|
Commercial bank prime lending rate:
|
15% (31 December 2007) |
|
Stock of money:
|
$2.616 billion (31 December 2007) |
|
Stock of quasi money:
|
$1.698 billion (31 December 2007) |
|
Stock of domestic credit:
|
$1.3 billion (31 December 2007) |
|
Agriculture - products:
|
coffee, cocoa, cotton, rubber, bananas, oilseed, grains, root starches; livestock; timber |
|
Industries:
|
petroleum production and refining, aluminum production, food processing, light consumer goods, textiles, lumber, ship repair |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
3.5% (2007 est.) |
|
Electricity - production:
|
3.903 billion kWh (2006 est.) |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
3.323 billion kWh (2006 est.) |
|
Electricity - exports:
|
0 kWh (2007 est.) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|
0 kWh (2007 est.) |
|
Electricity - production by source:
|
fossil fuel: 2.7%
hydro: 97.3% nuclear: 0% other: 0% (2001) |
|
Oil - production:
|
87,400 bbl/day (2008 est.) |
|
Oil - consumption:
|
24,500 bbl/day (2006 est.) |
|
Oil - exports:
|
108,800 bbl/day (2005) |
|
Oil - imports:
|
50,750 bbl/day (2005) |
|
Oil - proved reserves:
|
200 million bbl (1 January 2008 est.) |
|
Natural gas - production:
|
20 million cu m (2006 est.) |
|
Natural gas - consumption:
|
20 million cu m (2006 est.) |
|
Natural gas - exports:
|
0 cu m (2007 est.) |
|
Natural gas - imports:
|
0 cu m (2007 est.) |
|
Natural gas - proved reserves:
|
135.1 billion cu m (1 January 2008 est.) |
|
Current account balance:
|
-$325 million (2007 est.) |
|
Exports:
|
$3.827 billion f.o.b. (2007 est.) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|
crude oil and petroleum products, lumber, cocoa beans, aluminum, coffee, cotton |
|
Exports - partners:
|
Spain 19.8%, Italy 15.7%, France 11.7%, South Korea 9.4%, Netherlands 6.1%, US 5.7% (2007) |
|
Imports:
|
$3.714 billion f.o.b. (2007 est.) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|
machinery, electrical equipment, transport equipment, fuel, food |
|
Imports - partners:
|
France 23.4%, Nigeria 12.8%, China 9%, Belgium 5.8%, US 4% (2007) |
|
Economic aid - recipient:
|
$413.8 million (2005) |
|
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
|
$2.932 billion (31 December 2007 est.) |
|
Debt - external:
|
$2.554 billion (31 December 2007 est.) |
|
Market value of publicly traded shares:
|
$NA |
|
Currency (code):
|
Communaute Financiere Africaine franc (XAF); note - responsible authority is the Bank of the Central African States |
|
Currency code:
|
XAF |
|
Exchange rates:
|
Communaute Financiere Africaine francs (XAF) per US dollar - 493.51 (2007), 522.59 (2006), 527.47 (2005), 528.29 (2004), 581.2 (2003) |
| Communications | Cameroon |
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
130,700 (2006) |
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
4.536 million (2007) |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: fixed-line connections stand at less than 1 per 100 persons; equipment is old and outdated, and connections with many parts of the country are unreliable; mobile-cellular usage, in part a reflection of the poor condition and general inadequacy of the fixed-line network, increased more than 6-fold between 2002 and 2007 reaching a subscribership base of 25 per 100 persons
domestic: cable, microwave radio relay, and tropospheric scatter international: country code - 237; landing point for the SAT-3/WASC fiber-optic submarine cable that provides connectivity to Europe and Asia; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2007) |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
AM 2, FM 9, shortwave 3 (2001) |
|
Radios:
|
2.27 million (1997) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
1 (2001) |
|
Televisions:
|
450,000 (1997) |
|
Internet country code:
|
.cm |
|
Internet hosts:
|
69 (2008) |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
1 (2002) |
|
Internet users:
|
370,000 (2006) |
| Transportation | Cameroon |
|
Airports:
|
45 (2007) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 11
over 3,047 m: 2 2,438 to 3,047 m: 4 1,524 to 2,437 m: 3 914 to 1,523 m: 1 under 914 m: 1 (2007) |
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|
total: 34
1,524 to 2,437 m: 6 914 to 1,523 m: 20 under 914 m: 8 (2007) |
|
Pipelines:
|
gas 27 km; liquid petroleum gas 5 km; oil 1,110 km (2007) |
|
Railways:
|
total: 987 km
narrow gauge: 987 km 1.000-m gauge (2006) |
|
Roadways:
|
total: 50,000 km
paved: 5,000 km unpaved: 45,000 km (2004) |
|
Waterways:
|
navigation mainly on Benue River; limited during rainy season (2005) |
|
Ports and terminals:
|
Douala, Limboh Terminal |
| Military | Cameroon |
|
Military branches:
|
Cameroon Armed Forces: Army, Navy (includes naval infantry), Air Force (Armee de l'Air du Cameroun, AAC) (2008) |
|
Military service age and obligation:
|
18 years of age for voluntary military service; no conscription; the government makes periodic calls for volunteers (2006) |
|
Manpower available for military service:
|
males age 16-49: 4,321,175
females age 16-49: 4,228,625 (2008 est.) |
|
Manpower fit for military service:
|
males age 16-49: 2,567,428
females age 16-49: 2,498,990 (2008 est.) |
|
Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:
|
male: 212,205
female: 207,545 (2008 est.) |
|
Military expenditures:
|
1.3% of GDP (2006) |
| Transnational Issues | Cameroon |
|
Disputes - international:
|
Joint Border Commission with Nigeria reviewed 2002 ICJ ruling on the entire boundary and bilaterally resolved differences, including June 2006 Greentree Agreement that immediately ceded sovereignty of the Bakassi Peninsula to Cameroon with a full phase-out of Nigerian control and patriation of residents in 2008; Cameroon and Nigeria agree on maritime delimitation in March 2008; sovereignty dispute between Equatorial Guinea and Cameroon over an island at the mouth of the Ntem River; only Nigeria and Cameroon have heeded the Lake Chad Commission's admonition to ratify the delimitation treaty, which also includes the Chad-Niger and Niger-Nigeria boundaries |
|
Refugees and internally displaced persons:
|
refugees (country of origin): 20,000-30,000 (Chad); 3,000 (Nigeria); 24,000 (Central African Republic) (2007) |
|
Trafficking in persons:
|
current situation: Cameroon is a source, transit, and destination country for women and children trafficked for the purposes of forced labor and commercial sexual exploitation; most victims are children trafficked within country, with girls primarily trafficked for domestic servitude and sexual exploitation; both boys and girls are also trafficked within Cameroon for forced labor in sweatshops, bars, restaurants, and on tea and cocoa plantations; children are trafficked into Cameroon from neighboring states for forced labor in agriculture, fishing, street vending, and spare-parts shops; Cameroon is a transit country for children trafficked between Gabon and Nigeria, and from Nigeria to Saudi Arabia; it is a source country for women transported by sex-trafficking rings to Europe
tier rating: Tier 2 Watch List - Cameroon is on the Tier 2 Watch List for its failure to provide evidence of increasing efforts to combat human trafficking in 2007, particularly in terms of efforts to prosecute and convict trafficking offenders; while Cameroon reported some arrests of traffickers, none of them were prosecuted or punished; the government does not identify trafficking victims among vulnerable populations nor does it monitor the number of victims it intercepts (2008) |
|
This page was last updated on 18 December, 2008 |