


| The World Factbook | ||


|
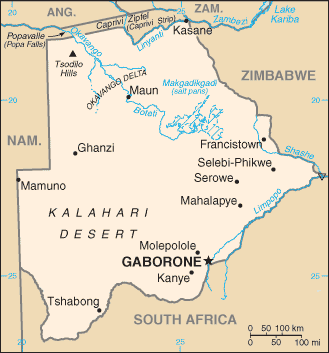
Botswana |

|
|
| Introduction | Botswana |
|
Background:
|
Formerly the British protectorate of Bechuanaland, Botswana adopted its new name upon independence in 1966. Four decades of uninterrupted civilian leadership, progressive social policies, and significant capital investment have created one of the most dynamic economies in Africa. Mineral extraction, principally diamond mining, dominates economic activity, though tourism is a growing sector due to the country's conservation practices and extensive nature preserves. Botswana has one of the world's highest known rates of HIV/AIDS infection, but also one of Africa's most progressive and comprehensive programs for dealing with the disease. |
| Geography | Botswana |
|
Location:
|
Southern Africa, north of South Africa |
|
Geographic coordinates:
|
22 00 S, 24 00 E |
|
Map references:
|
Africa |
|
Area:
|
total: 600,370 sq km
land: 585,370 sq km water: 15,000 sq km |
|
Area - comparative:
|
slightly smaller than Texas |
|
Land boundaries:
|
total: 4,013 km
border countries: Namibia 1,360 km, South Africa 1,840 km, Zimbabwe 813 km |
|
Coastline:
|
0 km (landlocked) |
|
Maritime claims:
|
none (landlocked) |
|
Climate:
|
semiarid; warm winters and hot summers |
|
Terrain:
|
predominantly flat to gently rolling tableland; Kalahari Desert in southwest |
|
Elevation extremes:
|
lowest point: junction of the Limpopo and Shashe Rivers 513 m
highest point: Tsodilo Hills 1,489 m |
|
Natural resources:
|
diamonds, copper, nickel, salt, soda ash, potash, coal, iron ore, silver |
|
Land use:
|
arable land: 0.65%
permanent crops: 0.01% other: 99.34% (2005) |
|
Irrigated land:
|
10 sq km (2003) |
|
Total renewable water resources:
|
14.7 cu km (2001) |
|
Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):
|
total: 0.19 cu km/yr (41%/18%/41%)
per capita: 107 cu m/yr (2000) |
|
Natural hazards:
|
periodic droughts; seasonal August winds blow from the west, carrying sand and dust across the country, which can obscure visibility |
|
Environment - current issues:
|
overgrazing; desertification; limited fresh water resources |
|
Environment - international agreements:
|
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
|
Geography - note:
|
landlocked; population concentrated in eastern part of the country |
| People | Botswana |
|
Population:
|
1,842,323
note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2008 est.) |
|
Age structure:
|
0-14 years: 35.2% (male 329,418/female 318,160)
15-64 years: 60.9% (male 566,239/female 556,286) 65 years and over: 3.9% (male 29,165/female 43,055) (2008 est.) |
|
Median age:
|
total: 21.2 years
male: 21 years female: 21.4 years (2008 est.) |
|
Population growth rate:
|
1.434% (2008 est.) |
|
Birth rate:
|
22.96 births/1,000 population (2008 est.) |
|
Death rate:
|
14.02 deaths/1,000 population (2008 est.) |
|
Net migration rate:
|
5.41 migrant(s)/1,000 population
note: there is an increasing flow of Zimbabweans into South Africa and Botswana in search of better economic opportunities (2008 est.) |
|
Sex ratio:
|
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
under 15 years: 1.03 male(s)/female 15-64 years: 1.02 male(s)/female 65 years and over: 0.68 male(s)/female total population: 1.01 male(s)/female (2008 est.) |
|
Infant mortality rate:
|
total: 44.01 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 44.94 deaths/1,000 live births female: 43.04 deaths/1,000 live births (2008 est.) |
|
Life expectancy at birth:
|
total population: 50.16 years
male: 51.28 years female: 49.02 years (2008 est.) |
|
Total fertility rate:
|
2.66 children born/woman (2008 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:
|
37.3% (2003 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:
|
350,000 (2003 est.) |
|
HIV/AIDS - deaths:
|
33,000 (2003 est.) |
|
Major infectious diseases:
|
degree of risk: high
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever vectorborne disease: malaria (2008) |
|
Nationality:
|
noun: Motswana (singular), Batswana (plural)
adjective: Motswana (singular), Batswana (plural) |
|
Ethnic groups:
|
Tswana (or Setswana) 79%, Kalanga 11%, Basarwa 3%, other, including Kgalagadi and white 7% |
|
Religions:
|
Christian 71.6%, Badimo 6%, other 1.4%, unspecified 0.4%, none 20.6% (2001 census) |
|
Languages:
|
Setswana 78.2%, Kalanga 7.9%, Sekgalagadi 2.8%, English 2.1% (official), other 8.6%, unspecified 0.4% (2001 census) |
|
Literacy:
|
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 81.2% male: 80.4% female: 81.8% (2003 est.) |
|
School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):
|
total: 12 years
male: 12 years female: 12 years (2005) |
|
Education expenditures:
|
8.7% of GDP (2007) |
| Government | Botswana |
|
Country name:
|
conventional long form: Republic of Botswana
conventional short form: Botswana local long form: Republic of Botswana local short form: Botswana former: Bechuanaland |
|
Government type:
|
parliamentary republic |
|
Capital:
|
name: Gaborone
geographic coordinates: 24 45 S, 25 55 E time difference: UTC+2 (7 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time) |
|
Administrative divisions:
|
9 districts and 5 town councils*; Central, Francistown*, Gaborone*, Ghanzi, Jwaneng*, Kgalagadi, Kgatleng, Kweneng, Lobatse*, Northeast, Northwest, Selebi-Pikwe*, Southeast, Southern |
|
Independence:
|
30 September 1966 (from UK) |
|
National holiday:
|
Independence Day (Botswana Day), 30 September (1966) |
|
Constitution:
|
March 1965, effective 30 September 1966 |
|
Legal system:
|
based on Roman-Dutch law and local customary law; judicial review limited to matters of interpretation; accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction, with reservations |
|
Suffrage:
|
18 years of age; universal |
|
Executive branch:
|
chief of state: President Seretse Khama Ian KHAMA (since 1 April 2008); Vice President Mompati MERAFHE (since 1 April 2008); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government
head of government: President Seretse Khama Ian KHAMA (since 1 April 2008); Vice President Mompati MERAFHE (since 1 April 2008) cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president elections: president indirectly elected for a five-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held 20 October 2004 (next to be held in October 2009); vice president appointed by the president election results: Festus G. MOGAE elected president; percent of National Assembly vote - 52% |
|
Legislative branch:
|
bicameral Parliament consists of the House of Chiefs (a largely advisory 15-member body with 8 permanent members consisting of the chiefs of the principal tribes, and 7 non-permanent members serving 5-year terms, consisting of 4 elected subchiefs and 3 members selected by the other 12 members) and the National Assembly (63 seats, 57 members are directly elected by popular vote, 4 are appointed by the majority party, and 2, the President and Attorney-General, serve as ex-officio members; members serve five-year terms)
elections: National Assembly elections last held 30 October 2004 (next to be held in October 2009) election results: percent of vote by party - BDP 51.7%, BNF 26.1%, BCP 16.6%, other 5%; seats by party - BDP 44, BNF 12, BCP 1 |
|
Judicial branch:
|
High Court; Court of Appeal; Magistrates' Courts (one in each district) |
|
Political parties and leaders:
|
Botswana Alliance Movement or BAM [Ephraim Lepetu SETSHWAELO]; Botswana Congress Party or BCP [Otlaadisa KOOSALETSE]; Botswana Democratic Party or BDP [Festus G. MOGAE]; Botswana National Front or BNF [Otswoletse MOUPO]; Botswana Peoples Party or BPP; MELS Movement of Botswana or MELS; New Democratic Front or NDF
note: a number of minor parties joined forces in 1999 to form the BAM but did not capture any parliamentary seats - includes the United Action Party [Ephraim Lepetu SETSHWAELO]; the Independence Freedom Party or IFP [Motsamai MPHO]; the Botswana Progressive Union [D. K. KWELE] |
|
Political pressure groups and leaders:
|
First People of the Kalahari (Bushman organization); Pitso Ya Ba Tswana; Society for the Promotion of Ikalanga Language (Kalanga elites)
other: diamond mining companies |
|
International organization participation:
|
ACP, AfDB, AU, C, FAO, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, Interpol, IOC, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC, MIGA, NAM, OPCW, SACU, SADC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNMIS, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO |
|
Diplomatic representation in the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Lapologang Caesar LEKOA
chancery: 1531-1533 New Hampshire Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20036 telephone: [1] (202) 244-4990 FAX: [1] (202) 244-4164 |
|
Diplomatic representation from the US:
|
chief of mission: Ambassador Stephen J. NOLAN
embassy: Embassy Enclave (off Khama Crescent), Gaborone mailing address: Embassy Enclave, P. O. Box 90, Gaborone telephone: [267] 395-3982 FAX: [267] 395-6947 |
|
Flag description:
|
light blue with a horizontal white-edged black stripe in the center |
| Economy | Botswana |
|
Economy - overview:
|
Botswana has maintained one of the world's highest economic growth rates since independence in 1966, though growth slowed to 4.7% annually in 2006-07. Through fiscal discipline and sound management, Botswana has transformed itself from one of the poorest countries in the world to a middle-income country with a per capita GDP of nearly $15,000 in 2007. Two major investment services rank Botswana as the best credit risk in Africa. Diamond mining has fueled much of the expansion and currently accounts for more than one-third of GDP and for 70-80% of export earnings. Tourism, financial services, subsistence farming, and cattle raising are other key sectors. On the downside, the government must deal with high rates of unemployment and poverty. Unemployment officially was 23.8% in 2004, but unofficial estimates place it closer to 40%. HIV/AIDS infection rates are the second highest in the world and threaten Botswana's impressive economic gains. An expected leveling off in diamond mining production overshadows long-term prospects. |
|
GDP (purchasing power parity):
|
$26.04 billion (2007 est.) |
|
GDP (official exchange rate):
|
$12.31 billion (2007 est.) |
|
GDP - real growth rate:
|
4.8% (2007 est.) |
|
GDP - per capita (PPP):
|
$14,300 (2007 est.) |
|
GDP - composition by sector:
|
agriculture: 1.6%
industry: 51.5% (including 36% mining) services: 46.9% (2006 est.) |
|
Labor force:
|
288,400 formal sector employees (2004) |
|
Labor force - by occupation:
|
agriculture: NA%
industry: NA% services: NA% |
|
Unemployment rate:
|
7.5% (2007 est.) |
|
Population below poverty line:
|
30.3% (2003) |
|
Household income or consumption by percentage share:
|
lowest 10%: NA%
highest 10%: NA% |
|
Distribution of family income - Gini index:
|
63 (1993) |
|
Investment (gross fixed):
|
19.2% of GDP (2007 est.) |
|
Budget:
|
revenues: $4.741 billion
expenditures: $3.816 billion (2007 est.) |
|
Fiscal year:
|
1 April - 31 March |
|
Public debt:
|
5.4% of GDP (2007 est.) |
|
Inflation rate (consumer prices):
|
7.1% (2007 est.) |
|
Central bank discount rate:
|
14.5% (31 December 2007) |
|
Commercial bank prime lending rate:
|
16.22% (31 December 2007) |
|
Stock of money:
|
$1.026 billion (31 December 2007) |
|
Stock of quasi money:
|
$4.336 billion (31 December 2007) |
|
Stock of domestic credit:
|
NA |
|
Agriculture - products:
|
livestock, sorghum, maize, millet, beans, sunflowers, groundnuts |
|
Industries:
|
diamonds, copper, nickel, salt, soda ash, potash; livestock processing; textiles |
|
Industrial production growth rate:
|
4.2% (2007 est.) |
|
Electricity - production:
|
979 million kWh (2006 est.) |
|
Electricity - consumption:
|
2.574 billion kWh (2006 est.) |
|
Electricity - exports:
|
0 kWh (2007 est.) |
|
Electricity - imports:
|
1.959 billion kWh (2007 est.) |
|
Electricity - production by source:
|
fossil fuel: 100%
hydro: 0% nuclear: 0% other: 0% (2001) |
|
Oil - production:
|
0 bbl/day (2007 est.) |
|
Oil - consumption:
|
11,640 bbl/day (2006 est.) |
|
Oil - exports:
|
0 bbl/day (2005) |
|
Oil - imports:
|
14,500 bbl/day (2005) |
|
Oil - proved reserves:
|
0 bbl (1 January 2006 est.) |
|
Natural gas - production:
|
0 cu m (2007 est.) |
|
Natural gas - consumption:
|
0 cu m (2007 est.) |
|
Natural gas - exports:
|
0 cu m (2007 est.) |
|
Natural gas - imports:
|
0 cu m (2007 est.) |
|
Natural gas - proved reserves:
|
0 cu m (1 January 2006 est.) |
|
Current account balance:
|
$1.973 billion (2007 est.) |
|
Exports:
|
$5.025 billion f.o.b. (2007 est.) |
|
Exports - commodities:
|
diamonds, copper, nickel, soda ash, meat, textiles |
|
Exports - partners:
|
European Free Trade Association (EFTA) 87%, Southern African Customs Union (SACU) 7%, Zimbabwe 4% (2006) |
|
Imports:
|
$3.403 billion f.o.b. (2007 est.) |
|
Imports - commodities:
|
foodstuffs, machinery, electrical goods, transport equipment, textiles, fuel and petroleum products, wood and paper products, metal and metal products |
|
Imports - partners:
|
Southern African Customs Union (SACU) 74%, EFTA 17%, Zimbabwe 4% (2006) |
|
Economic aid - recipient:
|
$70.89 million (2005) |
|
Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:
|
$9.79 billion (31 December 2007 est.) |
|
Debt - external:
|
$408 million (31 December 2007 est.) |
|
Market value of publicly traded shares:
|
$3.947 billion (2006) |
|
Currency (code):
|
pula (BWP) |
|
Currency code:
|
BWP |
|
Exchange rates:
|
pulas (BWP) per US dollar - 6.2035 (2007), 5.8447 (2006), 5.1104 (2005), 4.6929 (2004), 4.9499 (2003) |
| Communications | Botswana |
|
Telephones - main lines in use:
|
136,900 (2006) |
|
Telephones - mobile cellular:
|
1.427 million (2007) |
|
Telephone system:
|
general assessment: the system is expanding with the growth of mobile-cellular service and participation in regional development; system is fully digital with fiber-optic cables linking the major population centers in the east; fixed-line connections declined in recent years and now stand at roughly 8 per 100 persons; mobile-cellular telephone density currently is about 80 per 100 persons
domestic: small system of open-wire lines, microwave radio relay links, and a few radiotelephone communication stations; mobile-cellular service is growing fast international: country code - 267; international calls are made via satellite, using international direct dialing; 2 international exchanges; digital microwave radio relay links to Namibia, Zambia, Zimbabwe, and South Africa; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Indian Ocean) (2007) |
|
Radio broadcast stations:
|
AM 8, FM 13, shortwave 4 (2001) |
|
Radios:
|
252,720 (2000) |
|
Television broadcast stations:
|
2 (1 state-owned, 1 private) |
|
Televisions:
|
31,000 (1997) |
|
Internet country code:
|
.bw |
|
Internet hosts:
|
6,374 (2008) |
|
Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
|
11 (2001) |
|
Internet users:
|
80,000 (2007) |
| Transportation | Botswana |
|
Airports:
|
85 (2007) |
|
Airports - with paved runways:
|
total: 11
2,438 to 3,047 m: 2 1,524 to 2,437 m: 7 914 to 1,523 m: 2 (2007) |
|
Airports - with unpaved runways:
|
total: 74
1,524 to 2,437 m: 3 914 to 1,523 m: 54 under 914 m: 17 (2007) |
|
Railways:
|
total: 888 km
narrow gauge: 888 km 1.067-m gauge (2006) |
|
Roadways:
|
total: 25,798 km
paved: 8,410 km unpaved: 17,388 km (2005) |
| Military | Botswana |
|
Military branches:
|
Botswana Defense Force: Ground Forces, Air Wing (2008) |
|
Military service age and obligation:
|
18 is the apparent age of voluntary military service; the official qualifications for determining minimum age are unknown (2001) |
|
Manpower available for military service:
|
males age 16-49: 487,853
females age 16-49: 464,278 (2008 est.) |
|
Manpower fit for military service:
|
males age 16-49: 290,093
females age 16-49: 257,700 (2008 est.) |
|
Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:
|
male: 23,007
female: 22,551 (2008 est.) |
|
Military expenditures:
|
3.3% of GDP (2006) |
| Transnational Issues | Botswana |
|
Disputes - international:
|
Botswana still struggles to seal its border from thousands of Zimbabweans who flee economic collapse and political persecution; Namibia has long supported, and in 2004 Zimbabwe dropped objections to, plans between Botswana and Zambia to build a bridge over the Zambezi River at Kazungula crossing, thereby de facto recognizing the short, but not clearly delimited, Botswana-Zambia boundary |
|
This page was last updated on 18 December, 2008 |